
A state-of-the-art coupled physical-biogeochemical model tailored for the Red Sea was developed, implemented on the KAUST supercomputing facility – SHAHEEN, and successfully tested and validated to simulate the ecosystem variability in the Red Sea basin. This unique model is composed of the MIT ocean general circulation model (MITgcm), which has been extensively used by our group to simulate and study the general circulation and physical variability of the Red Sea, and the NBLING biogeochemistry model to simulate the interactions between biological, chemical, and physical processes. The coupled model was configured at a high spatial horizontal resolution of 1 km and 65 layers vertically to resolve the Red Sea ecosystem variability across diel, seasonal, and interannual scales.
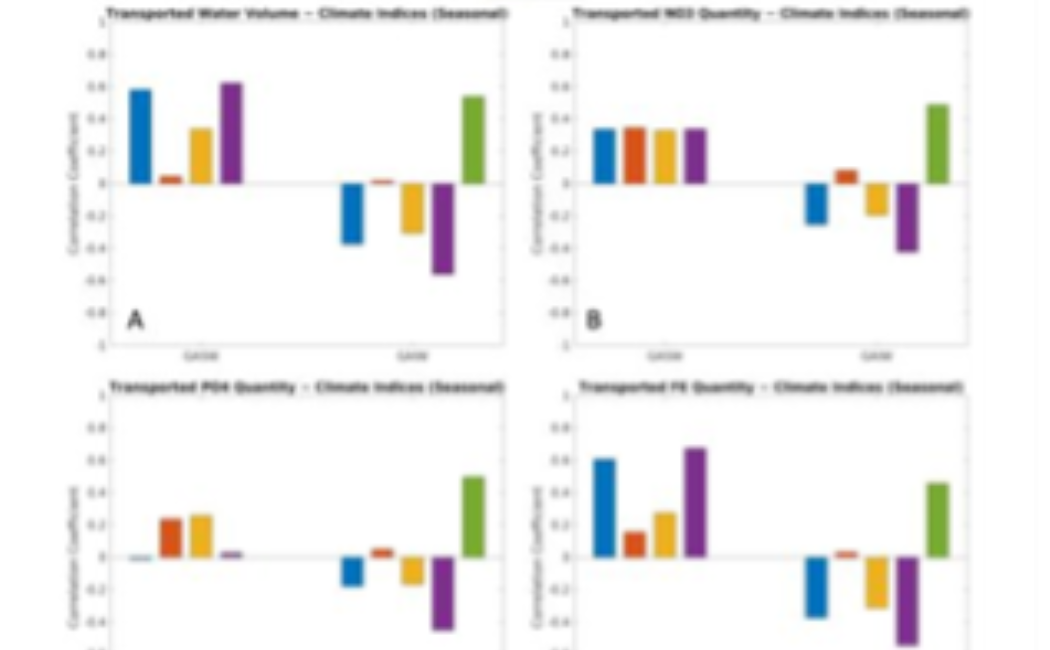
Analysis based on long-term model simulations enables us to investigate various scientific questions related to the variability of the Red Sea ecosystem, such as the interannual variability in nutrient supply from the Gulf of Aden and its relationship with global climate drivers (e.g., ENSO). The model outputs, together with a previously developed in-house physical connectivity model, were further combined to develop a seascape genetic model. This model examines the theories of Isolation by Distance (IBD), Isolation by Circulation (IBC), and Isolation by Environment (IBE) in the Red Sea.Dreano, D., Raitsos, D. E., Gittings, J., Krokos, G., & Hoteit, I. (2016). The Gulf of Aden Intermediate Water Intrusion Regulates the Southern Red Sea Summer Phytoplankton Blooms. PLOS ONE, 11(12), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0168440
Triantafyllou, G., Yao, F., Petihakis, G., Tsiaras, K. P., Raitsos, D. E., & Hoteit, I. (2014). Exploring the Red Sea seasonal ecosystem functioning using a three-dimensional biophysical model. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(3), 1791–1811. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JC009641